# 手写冒泡算法
function bubbleSort(arr) {
const len = arr.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 每次排序一轮,就排序好一个元素
for(let j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
const temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
# 根据 value 获取叶子节点
/**
* 获取树节点
* @param {Array} tree 树结构
* @param {*} value 要找的节点值
* @param {String} keyName 要找的节点键名
* @param {String} childrenKey 当前节点中子节点键名
*/
export function getTreeNode(tree, value, keyName, childrenKey) {
const stack = [...tree];
let tempNode;
while (stack.length) {
tempNode = stack.pop();
if (tempNode[keyName] === value) {
return tempNode
}
if (tempNode[childrenKey] && tempNode[childrenKey].length) {
stack.push(...tempNode[keyName]);
}
}
return null;
}
# 根据 value 获取叶子节点的路径
/**
* 根据 value 获取叶子节点的路径
* @param {Array} tree
* @param {*} value
* @param {String} keyName
* @param {String} childrenKey
*/
export function getTreeKeyPath(tree, value, keyName, childrenKey = 'children') {
const path = [];
const parse = (subTree) => {
for (let i = 0; i < subTree.length; i += 1) {
const node = subTree[i];
path.push(node[keyName]);
if (node[keyName] === value) {
return true;
}
if (node[childrenKey] && node[childrenKey].length) {
if (parse(node[childrenKey])) {
return true;
}
}
path.pop();
}
return false;
};
parse(tree);
return path;
}
# 列表结构转树结构
# 递归
使用该方法虽然易懂,但是当 source 列表比较大的时候性能会比较差。
export function listToTree(source, pid = 0) {
const list = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(source)); // 避免影响之前的数组
const result = [];
list.forEach(item => {
if (item.parentId === pid) {
item.children = listToTree(source, item.id);
result.push(item);
}
});
return result;
}
# 循环
该方法比上面的递归性能更好。
export function listToTree(source, rootId = 0) {
const list = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(source)); // 避免影响之前的数组
const map = new Map();
const result = [];
list.forEach((item) => {
// 如果父节点在后面出现,需要合并 children 属性
item = { ...item, ...map.get(item.id) };
map.set(item.id, item);
if (item.id === rootId) {
result.push(item);
} else {
const parentItem = map.get(item.parentId) || {};
if (!parentItem.children) {
parentItem.children = [];
}
parentItem.children.push(item);
map.set(item.parentId, parentItem);
}
});
return result;
}
# 实现洗牌算法
// 返回最小与最大值之间的随机数,包含最大最小值
function getRandomInt(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) + min);
}
//将数组的副本循环随机打乱重组一个新数组返回
//实现方法: 在[0~i]数组中,取出i的值,将他的值与随机一个小于i索引的值对换
export function shuffle(arr) {
let _arr = arr.slice();
for (let i = 0; i < _arr.length; i++) {
let j = getRandomInt(0, i);
let t = _arr[i];
_arr[i] = _arr[j];
_arr[j] = t;
}
return _arr;
}
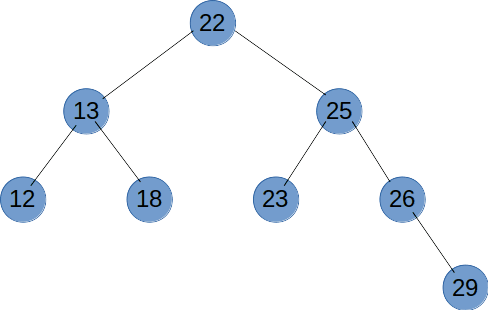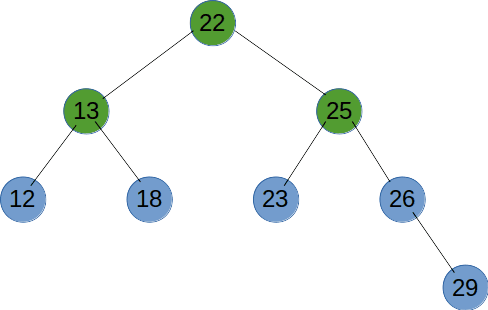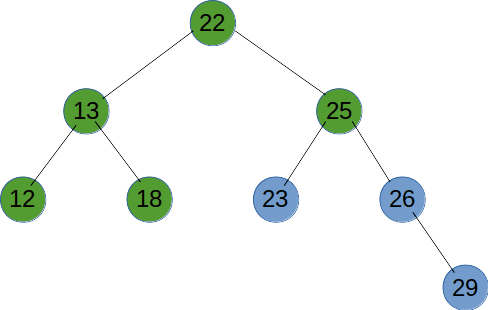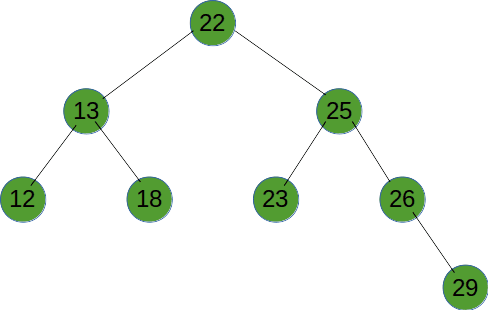
# 二叉树遍历(前序、中序、后序、广度优先)
# 前序遍历
前序遍历是先输出节点的值,再递归遍历左右子树,前序遍历是一个深度优先的遍历方法。
function recursionTreeNode(root) {
if (root != null) {
console.log(root.val);
recursionTreeNode(root.left);
recursionTreeNode(root.right);
}
}
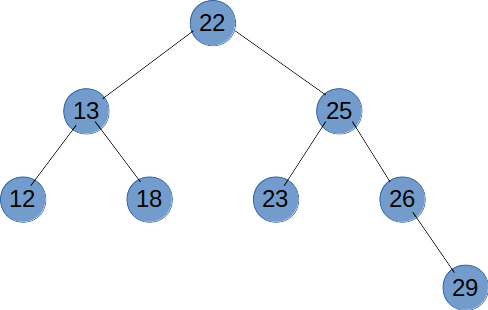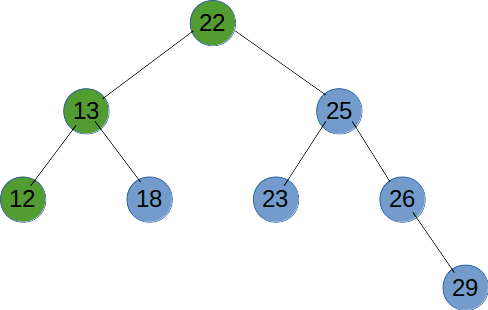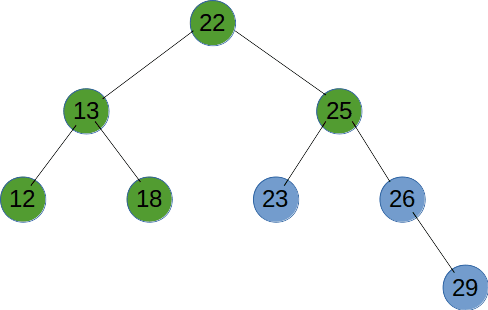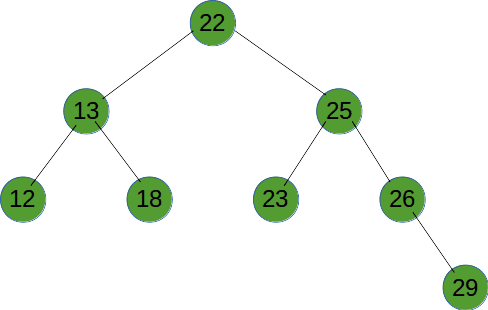
# 中序遍历
中序遍历是先遍历左子树,再输出当前节点,最后遍历右子树。
function recursionTreeNode(root) {
if (root != null) {
recursionTreeNode(root.left);
console.log(root.val);
recursionTreeNode(root.right);
}
}
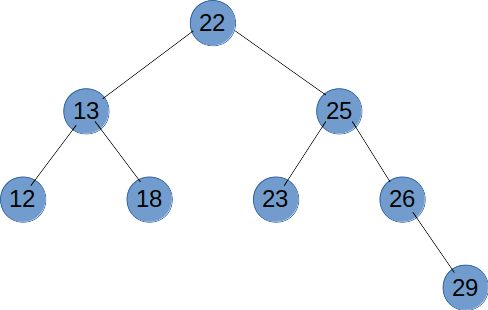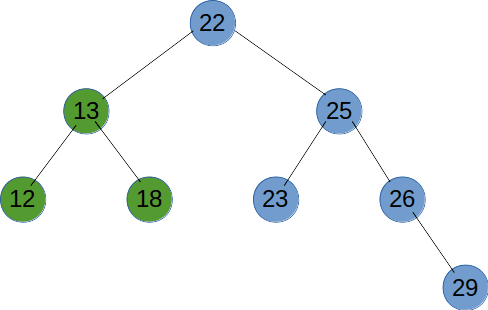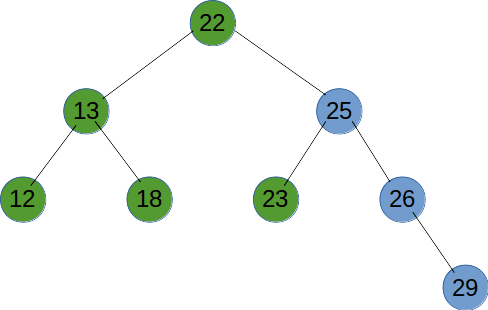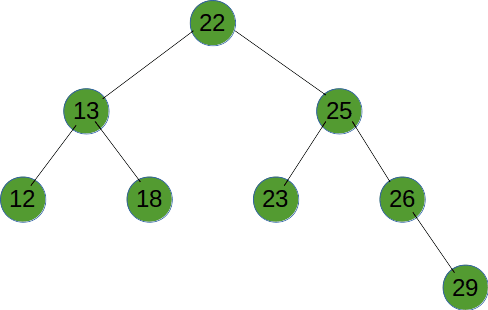
# 后序遍历
后序遍历是先递归遍历左右子树,再输出节点的值。
function recursionTreeNode(root) {
if (root != null) {
recursionTreeNode(root.left);
recursionTreeNode(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
}
}
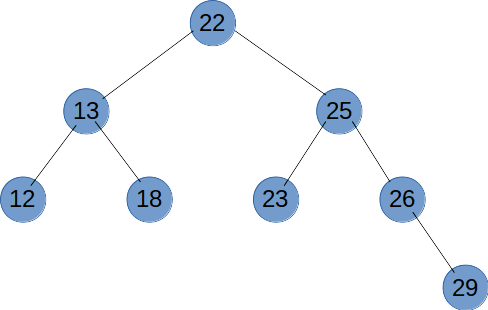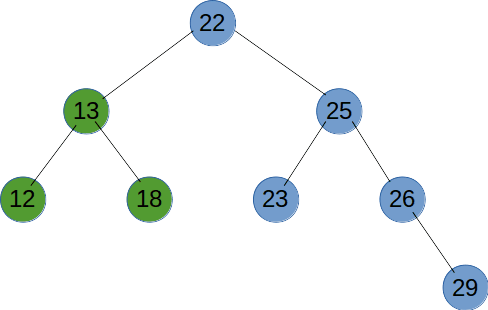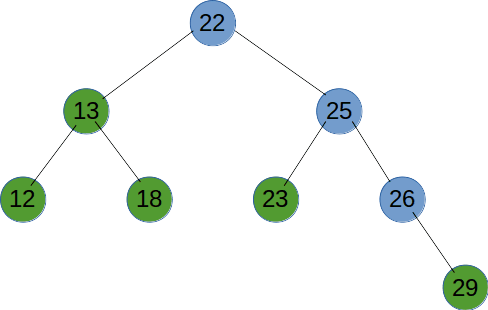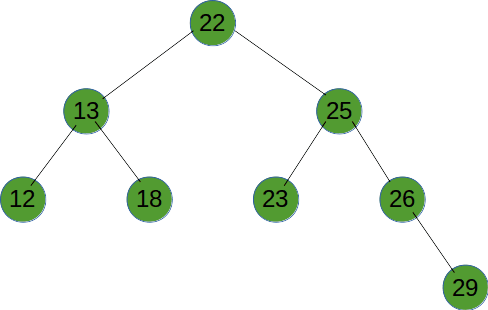
# 广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历就是按树的深度,从根节点开始,一层一层向底部遍历。
function recursionTreeNode(root) {
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
let tempNode = stack.pop();
console.log(tempNode.val)
if (tempNode.children.length) {
stack.push(...tempNode.children);
}
}
return null;
}